In this article, I list the ten reasons industrial automation equipment can improve any company’s manufacturing process, the importance of automation, the disadvantages, and where to find staffing support.
The top 10 reasons for industrial automation.
Growing revenue can be difficult due to high operative costs. Therefore, learning how to reduce costs while maintaining product quality, increasing employee satisfaction, reducing scrap, and decreasing downtime is essential. Automating processes is an integral step in expanding a company’s manufacturing capabilities.
Automating your production line will help you increase your revenue and improve the quality of your products. Every business must consider incorporating industrial automation into its automated manufacturing process.
What is industrial automation?
First, I need to explain to you what an industrial automation system is. Industrial automation refers to using technology and control systems to automate various industrial processes and automate tasks while reducing the need for human intervention. It involves the application of advanced hardware and software systems to help inefficient production lines, increase productivity, improve accuracy, and have safer industrial operations.
Industrial automation encompasses various activities, including manufacturing, assembly lines, material handling, packaging, quality control, and even complex industrial processes. The main objective is to streamline and optimize these processes by integrating the components below into one cohesive system.
Key automation components commonly associated with industrial automation:
- Sensors And Actuators: Sensors detect physical variables such as temperature, pressure, position, or proximity, while actuators are devices that initiate physical actions based on signals from the control system.
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): Programmable logic controllers are specialized computers that monitor and control industrial processes. They receive sensor input, make decisions based on predefined logic, and send commands to actuators.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): HMIs provide a graphical interface for operators to monitor and interact with the automation system. They display real-time data, allow for manual control, and provide information for troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition (SCADA): SCADA systems enable centralized monitoring and control of multiple industrial processes. They collect data from various sensors and provide a high-level view of the entire operation, allowing operators to make informed decisions.
- Robotics And Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Industrial robots are used extensively in industrial automation to perform repetitive tasks with precision and speed. Robotic process automation uses software bots to automate rule-based, repetitive tasks that humans traditionally perform.
- Internet Of Things (IoT): IoT technology enables the connection of various devices and systems, allowing for data exchange and control over the Internet. This connectivity can enhance automation by enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making.
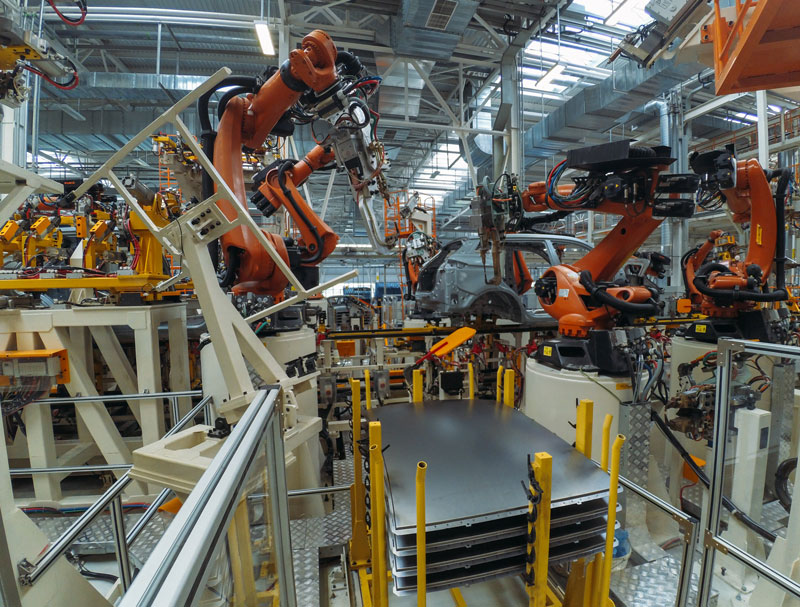

The top 10 reasons to purchase industrial automation equipment:
#1 It Can Create A Safer Work Environment:
The first and most important reason to invest in industrial automation is that manufacturing jobs can be dangerous. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, in 2021, there were 383 fatal work injuries in the manufacturing sector. Many of these may have been prevented by following proper safety procedures or using industrial automation equipment.
The industrial automation process allows robots to handle high-risk tasks while humans can perform lower-risk tasks on the assembly line. A good example is industrial robots, which can lift and move heavy objects while the operators insert small plastic parts into the object.
Manufacturing companies with a safety-first mentality will automate dangerous jobs to protect their employees.
#2 Incoming Labor Shortages:
The reality of labor shortages in America is very serious, especially post-pandemic. According to the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM), the manufacturing sector is expecting 2.1 million unfilled manufacturing jobs by 2030, because of a shortage of skilled workers.
Automation can fill in some of these workforce gaps and prevent labor shortages from affecting an organization. These missing jobs could cost the company millions in production, and the organization must be adequately prepared to handle these shortages.
#3 Automation Allows Product Flexibility:
Automation allows a company to change its production line at any time rapidly. For example, changing a product on a manual assembly line could take several hours, but it would only be clicking a button on an automated process. The robots in the automated system would know that a different product was in the production line and what needs to be done differently to this product.
A significant shift in production suddenly becomes a matter of minutes for technical maintenance staff instead of hours of changes and planning.
#4 Improved Assembly Line Efficiencies:
Any time industrial automation is used, it will improve the efficiency of the assembly line.
The organization will see improvements by:
- The quality of products will increase
- Changing of products on the assembly line
- Increased product output
- Staff will become more technical
- A decrease in downtime
- Plant safety will increase
- Scrap material reduction
#5 Decrease of Human Error:
Automation eliminates most human errors on any production line. Industrial robots use exceptionally accurate equipment and thrive with highly repeatable tasks or operations.
Even with proper training, human error can still cause revenue losses for companies. In a study performed by Vanson Bourne, they found that 23% of all unscheduled downtime in the manufacturing sector, was caused by human error.
The goal of an organization is to limit the number of unplanned human errors. With automation, many of these human-related errors can be reduced.
The best way to improve inefficient production lines is by reducing all errors caused by humans interrupting the line.
#6 Cycle Time Reduction:
Reducing lead times between customer orders and shipments naturally results from increased production efficiency. An automated assembly line will provide the efficiencies required to help reduce cycle times, which leads to a decrease in lead times.
If an organization can reduce its overall cycle times, more products can be manufactured and supplied to customers, increasing profitability.
#7 Automation Can Save The Business Money:
Automation will save the company money, but this is no secret. It may not seem obvious initially because of the high cost of initial capital that must be invested in robots and equipment. Still, the long-term savings can be significant over the product’s life cycle.
Assembly line efficiency is the number 1 factor of automation profitability. When businesses reduce downtime, they can save thousands of dollars an hour in potentially lost profits.
The real question is, how much money can industrial automation save the company? That answer varies on the type of products, the number of products made, the length of the build cycle, and margins. Most companies will start to save money by year three, which could be in the hundreds of thousands or millions of dollars.
#8 The Ability To Have Data Collection:
Most automated devices have data collection capabilities. Compared to a labor workforce assembly line, automated production lines allow accessible data collection through the equipment.
In most companies, data is the foundation of any business, whether it is in finance, sales, or manufacturing production. With the data companies want to know the data to make strategic moves within their industry. Data in industrial automation is critical to analyze daily, weekly, and monthly to see where productivity improvements can be accomplished within the line.
#9 Conditions For Workers Are Improved:
Robots and other industrial equipment are great at handling simple, repetitive, dangerous, or heavy tasks. This allows a company’s labor force to focus on other facility-related tasks.
The employees will be happier if given creative tasks than merely performing their daily monotonous tasks. These jobs can lead to boredom, which can make a person unfocused and cause factory accidents.
#10 Operation Improvements:
The data can be used to adjust the production line and increase throughput in industrial automation processes. Any adjustment to increase the speed and decrease cycle times will improve the overall operations of any system. Robot paths and PLC signals are often the first things identified when trying to improve line production.
What is the importance of industrial automation?
You might be asking yourself, why is industrial automation important? Industrial automation is vital for manufacturing for the key reasons I list below.
- Increased Efficiency And Productivity: Automation reduces manual labor and streamlines the industrial process, leading to higher production efficiency. Automated systems can perform tasks faster, more accurately, and more consistently than human operators. This leads to optimized production cycles, reduced downtime, and increased throughput.
- Improved Product Quality: Automation technology eliminates the risk of human error and variations in industrial processes. It ensures precise and consistent execution of tasks, resulting in reduced defects and improved product quality. Automated systems can perform quality checks and adjustments in real-time, leading to higher production standards and customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Workplace Safety: Industrial automation reduces workers’ exposure to hazardous or physically demanding tasks. Automating dangerous or repetitive tasks significantly reduces the risk of workplace accidents and injuries. This promotes a safer working environment and protects the well-being of the company’s employees.
- Increased Production Capacity And Flexibility: Automation enables industries to scale their production capacity. Automated systems can operate 24/7, allowing for continuous production and increased output. Additionally, automation provides greater flexibility by enabling quick reconfiguration and change of production lines to accommodate product variations. This agility helps companies to meet market demands effectively and quickly.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Industrial automation generates vast amounts of data related to production processes, equipment performance, and quality metrics. This data can be analyzed in real-time to gain insights, identify bottlenecks, and optimize operations. Data-driven decision-making enables continuous improvement, predictive maintenance, and proactive problem-solving, leading to higher operational efficiency and improved decision-making processes.
- Technological Advancements And Company Innovation: Automation encourages technological advancement and innovation within the manufacturing industry. It drives the development of new technologies, such as industrial robotics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), further enhancing industrial processes. Companies that embrace automation gain a competitive edge by adopting these cutting-edge technologies and staying at the forefront of industry trends.
- Skilled Workforce Development: While an automation solution may replace specific manual tasks, it also creates new opportunities for workers to develop their skills. It requires skilled personnel to operate, program, and maintain these automated systems. As industries adopt automation, there is a growing demand for a highly skilled workforce with expertise in robotics, programming, data analytics, and system integration. Automation promotes skill development, upskilling, and reskilling, leading to a more technologically proficient workforce.
What are the disadvantages of industrial automation in manufacturing?
While I highlighted numerous benefits of industrial automation above, it would be disingenuous not to share some potential disadvantages when considering it in any manufacturing automation process. Here are a few critical disadvantages of industrial automation in manufacturing:
- High Initial Investment: Implementing industrial automation systems can require a significant upfront investment. The cost of purchasing and installing automation equipment, industrial robots, software, and infrastructure and the expenses associated with system integration and eventual training can be massive, depending on the project size. This initial cost may pose a financial barrier for small and medium-sized companies.
- Technological Complexity: Automation systems involve complex technologies, including hardware, software, and connectivity. Designing, implementing, and maintaining these systems often requires specialized technical expertise. Companies may need to hire or train employees with the necessary skills, which can add to automation adoption’s overall cost and complexity. If your company is looking for skilled contract engineering services, check out JOINER Services for your labor support.
- Dependency On Technology: Industrial automation technology relies heavily on its devices, and any disruptions or malfunctions in the automation systems can lead to production downtime. Companies must have backup plans and contingency measures to reduce the risks associated with automation system failures, technical glitches, or unscheduled downtime. Maintaining and troubleshooting automation systems may require specifically trained technical support and skilled emergency resources.
- Reduced Customization: Automation systems are typically designed for specific tasks or processes. While they excel at repetitive and standardized operations, they may need more flexibility for customization or adaptation to rapidly changing production process requirements. Reconfiguring or reprogramming automation systems to accommodate new product variations or process changes can be time-consuming and costly.
- Impact On Employment: Industrial automation can lead to job displacement or changes in the workforce structure. Automation replaces specific manual tasks previously performed by humans, which may reduce labor requirements and costs. This can create concerns about job loss and the need for reskilling or upskilling displaced workers for new roles in a more technologically advanced workplace environment.
- Required Maintenance: Automated systems require regular maintenance, updates, and calibration to ensure optimal performance. This includes periodic inspections, equipment servicing, and software updates. Companies must allocate resources and budget for ongoing maintenance and preventive daily, weekly, monthly, and annual measures to address the wear and tear of the automated machines.
- Potential For Data Risks: As automation systems become more interconnected and reliant on digital technologies through the Internet, and they are susceptible to cybersecurity threats. Unauthorized access, data breaches, or malicious attacks on industrial control systems can pose risks to production processes, intellectual property, and sensitive data. Robust cybersecurity measures and continuous monitoring are essential to mitigate these risks.
Each company needs to determine what they consider essential factors when using automation. While there are disadvantages to industrial automation, many of these challenges can be managed with strategic planning, implementation strategies, and ongoing support. Automation’s overall impact and trade-offs should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, considering each company’s specific needs, goals, and circumstances.
When should you consider industrial automation labor support?
You should bring in industrial automation labor support when your operation requires specialized expertise, faces tight deadlines, or undergoes major changes. If your team lacks experience in areas like PLC programming, robotics integration, or HMI development, contract automation professionals can fill those gaps quickly.
Tight timelines for installations, upgrades, or commissioning often demand extra hands with the right technical knowledge to keep things on track. When launching or reconfiguring production lines, having experienced automation staff ensures smoother transitions and faster troubleshooting. As your operation scales, so does the demand for skilled labor. Contract support helps manage the increased workload without long-term commitments.
Automation labor is also ideal when testing or implementing new technologies. Instead of retraining your in-house team, you can bring in experts who already know the systems. For businesses that value flexibility, short-term or project-based automation contracting services offer the ability to adjust staffing levels based on workload, budget, or technical needs.
Whether it’s a large capital project, a shift toward Industry 4.0, or simply the need to improve production efficiency, bringing in industrial automation labor support can save time, reduce errors, and help you stay competitive. It’s a smart, scalable solution when internal resources are stretched or specific expertise is needed.
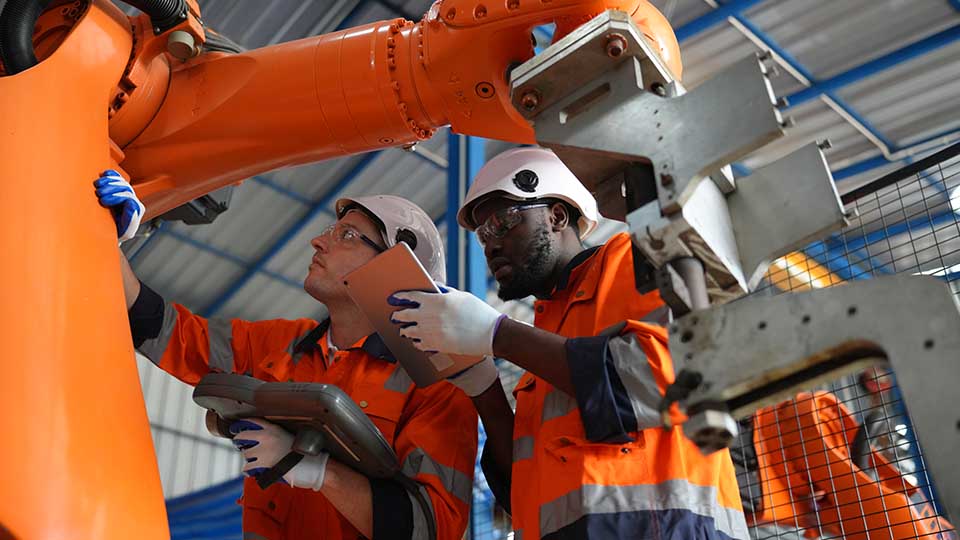

Where to find industrial automation contract labor support?
If your business needs experienced and professional contract engineers to help install an automated production line, look to JOINER Services to find those qualified individuals. Your company will build the most efficient automation line using its engineering services platform to find your contract labor.

Join today for free, and find the industrial automation support you need!
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
Below, I describe FAQs about the industrial automation industry.
Data Resources:
- [1] https://www.bls.gov/charts/census-of-fatal-occupational-injuries/number-and-rate-of-fatal-work-injuries-by-industry.htm
- [2] https://www.nam.org/2-1-million-manufacturing-jobs-could-go-unfilled-by-2030-13743/?stream=workforce
- [3] https://www.engineering.com/story/human-error-is-worse-in-manufacturing-compared-to-other-sectors








