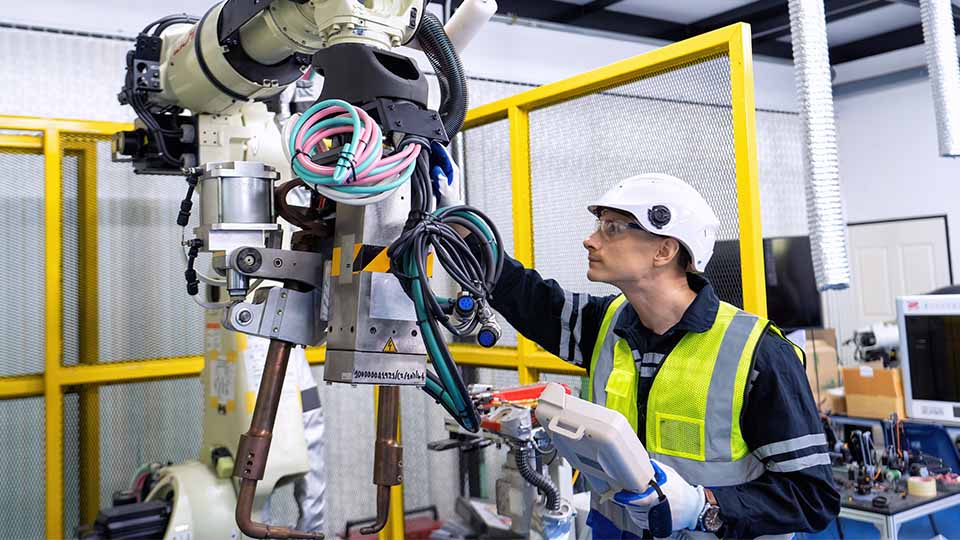
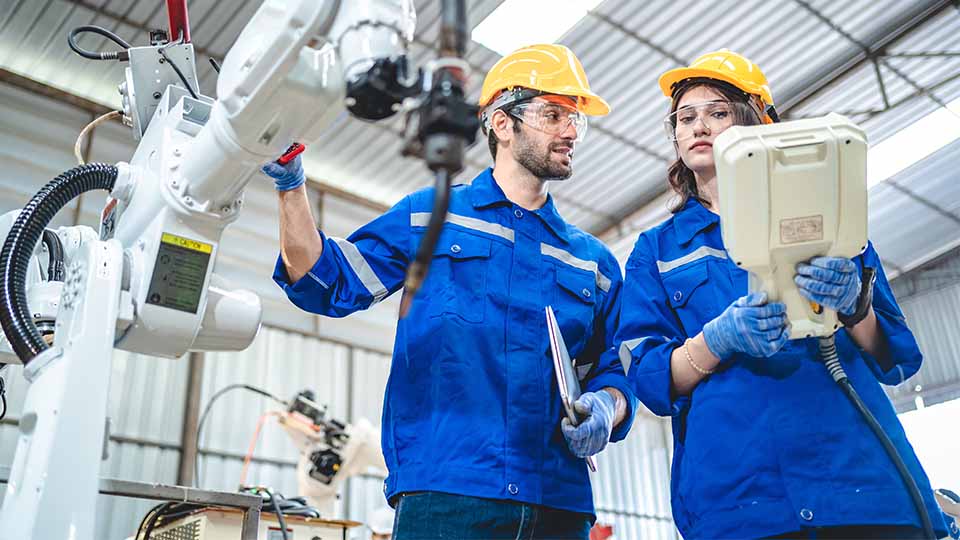
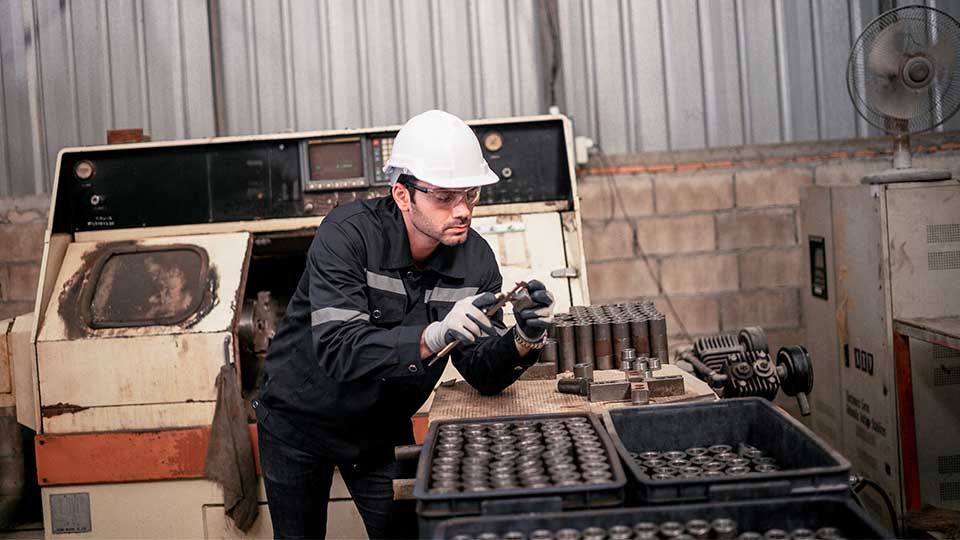
Welding automation is shaping the future of industrial manufacturing, but the area of welding technology is not as new as you may think. There’s still a lot to learn before applying it to your operations.
Here’s everything you will need to know about welding automation, including its greatest advantages, the potential disadvantages, pre-implementation, and welding installation requirements.
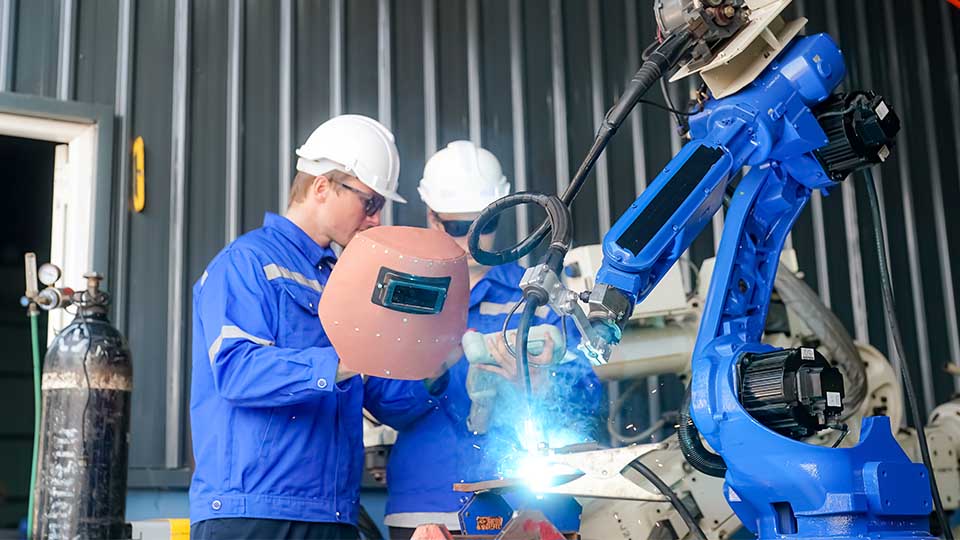

What is welding automation?
Welding automation equipment, such as welding robots, has modernized the entire welding industry. Even in its simplest form, this advanced welding technology can significantly improve efficiency, consistency, safety, and, ultimately, the welding quality of the end products.
At the core of welding automation, you will find automation systems ranging from straightforward semi-automatic machines—great for knocking out consistent welds—to sophisticated robotic welding arms that can navigate complex tasks on varied components.
Fully Automated Welding vs. Semi-Automated Welding Systems:
Fully Automated Welding Equipment: This is the “set it and forget it” solution in the welding world. These welding systems are designed to handle the entire welding process from start to finish without any human intervention.
You program the welding tasks into the automated welding machine, and it executes the robot welding according to the precise specifications. Such a setup is ideal for large-scale production environments where consistency and volume are a must.
Semi-Automated Welding Systems: These automated systems still require a human touch. They automate part of the welding process but rely on a skilled operator to manage or oversee critical parts of the welding application.
This might involve setting up the part on a fixture, continuously monitoring the welding operation, and adjusting welding parameters as needed during the job.
Semi-automated systems strike a balance between automation and flexibility, which makes them suitable for workshops that handle a large variety of welding tasks or where each piece might require a slightly different approach.
However it is important to note that some types of welding systems can be both fully automatic and semi-automatic, such as submerged arc welding (SAW).
Automated Welding vs. Robotic Welding:
Automated Welding: This refers more broadly to any welding process that uses welding equipment to automate part or all of the welding task. This includes everything from simple mechanized equipment for simple yet repetitive tasks to complex assemblies that integrate several automated functions.
Robotic Welding: This involves specific types of automated systems like robotic arms attached to welding guns and equipped with a welding power supply. The welding system can then be programmed to weld on a spot-by-spot basis while the welding robot performs the repetitive motions. Click this link to learn more details about robotic welding.
This welding technology is particularly valuable in industries where the welding requirements are complex and varied because they require rapid welding and part flexibility.
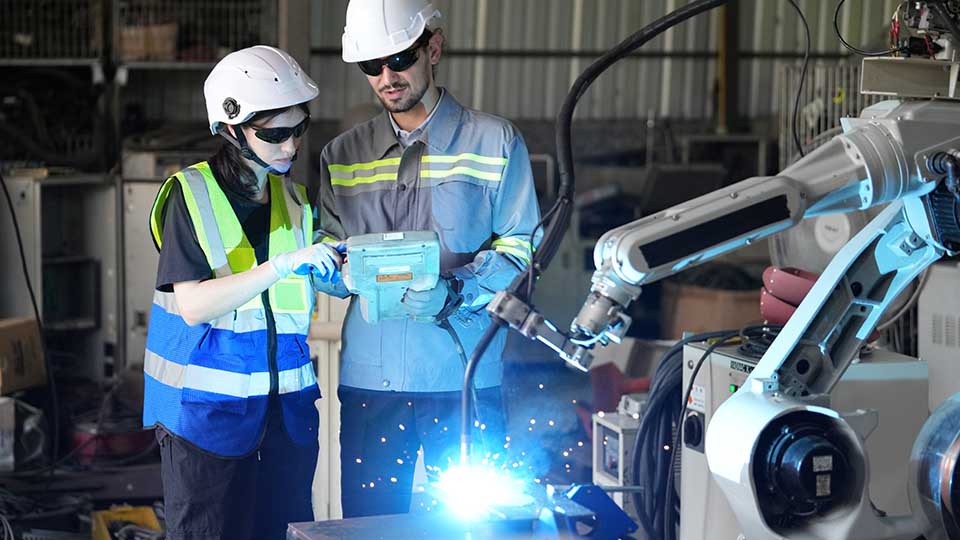

What are the advantages of welding automation?
Automation is taking over the manufacturing and welding industry for a lot of good reasons. When comparing automated welding processes to manual welding processes, you will notice the following benefits:
- Better Productivity: Automated systems don’t need lunch or bathroom breaks or even eight hours of sleep every night. They keep chugging along at a much faster rate than humans, which means more can get done in less amount of time.
- Consistency: As long as the parts and tooling are consistent, every weld will be consistent because the automated machines follow the exact same programmed weld path every time.
- Safer Work Environment: Welding can be dangerous, with all the heat, sparks, fumes, and confined spaces. Automation takes care of the hazardous tasks, making the workplace safer for humans.
- Less Waste, More Savings: When welding machines get the measurements right the first time, there is less material thrown out as scrap or waste. Such a level of precision saves materials and cuts down on waste costs.
- Smarter Use Of Labor: With automated welding machines handling the repetitive work, skilled manual welders can focus on more complex or creative tasks. Automated machines can potentially address a company’s skilled labor shortages. A company can then take its skilled tradespeople to robot programmer training classes and increase wages, which increases job satisfaction.
What are the potential disadvantages of robotic welding?
Of course, purchasing and implementing robotic welding system is not easy. Here are a few potential issues that you should consider before purchasing:
- Initial Capital Cost: Setting up an automated welding process is not cheap. The initial costs for the welding equipment and getting everything up and running can be steep, which might be difficult for smaller shops to justify the cost.
- Complex Setup And Maintenance: These systems can be complex to integrate and require regular maintenance to keep them running smoothly. This means you need people who are not just skilled manual welders but also a staff that is qualified to handle troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Flexibility Issues: Automated systems are great at doing repetitive welds, but if you frequently switch between different types of welding jobs or work with custom pieces, the rigidity of automation might be a big hindrance.
- Training Requirements: Implementing automation also involves training your team to use it the right way. This can add to the upfront costs and the time it takes before you start seeing a return on your investment.
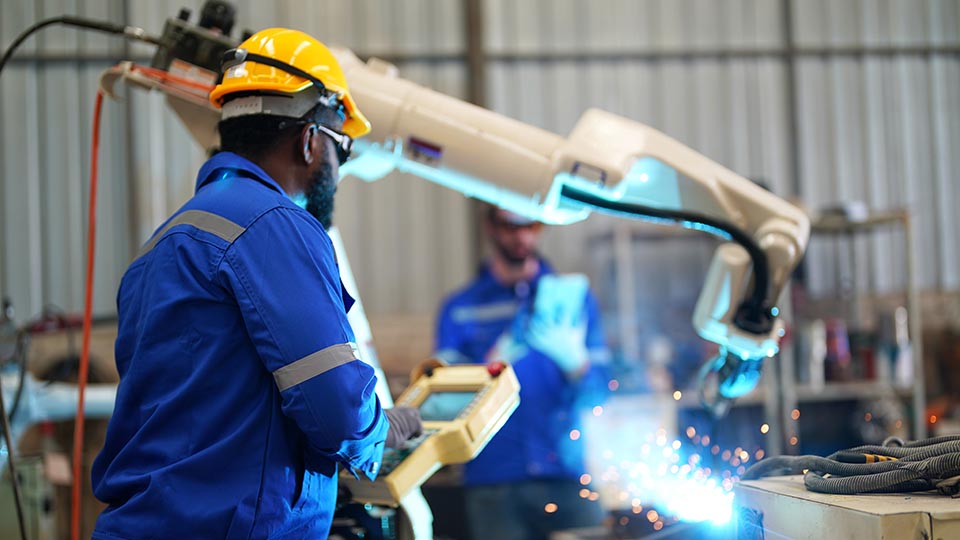

Types of welding automation:
Below, I list a few of the common types of welding automation processes:
- MIG Welding
- TIG Welding
- Laser Welding
- Spot Welding
- Submerged Arc Welding
- Plasma Welding
3 things to know before investing in automatic welding.
Aside from the pros and cons I have mentioned above, what else should you know before investing in this type of automation equipment?
#1 It Won’t Replace All Human Welders:
The idea that robots are coming for all our jobs is a bit overblown, especially in the welding industry. While automatic welding systems can take over many repetitive and high-volume tasks, they lack the problem-solving capabilities and adaptability of a skilled human welder.
Complex or custom jobs, highly remote working areas, one-off builds, and extreme quality control are operations that require nuanced judgment and are still best handled best by manual welding.
#2 You Need to Prepare for the Upfront Costs:
The costs are not just limited to purchasing the automated machines. You will also need to consider the expenses related to installing the system, training employees to operate the new technology, and possibly upgrading your facility’s infrastructure to accommodate the new automation equipment into the current assembly line.
#3 Finding an Automation Expert is a Non-Negotiable:
Implementing an automated welding system is complex and involves both the integration of new technology and a shift in your team’s approach to welding tasks.
That said, finding engineering contractors is a must. They have the experience to ensure that the system is set up correctly, train your team, and help troubleshoot any issues that arise during installation. An expert contract weld engineer can provide invaluable insights into the best type of automation for your specific welding needs and help you avoid costly pitfalls.
Welding Automation Jobs:
Welding automation jobs can be found across many job boards, like Indeed, or ZipRecruiter, if you are looking for full-time employment. Welding automation jobs can vast range in pay scale depending on the location of the job, experience required, and types of welding automation used.
If you are a welding engineer or weld technician and want to find contract welding automation jobs, look to engineering service platforms like JOINER Services to find welding engineering jobs. They offer a robust opportunity for welding jobs that you can view after creating a personalized profile.
Four key factors that are driving the advancement of industrial welding robots.
The future of welding automation is exciting to think about. Welding robots will play a significant role in product manufacturing for years to come. These are the four key factors driving the advancement of industrial welding robots:
- Improved Productivity: Industrial welding automation can help to improve a company’s productivity by automating simple welding tasks. With proper setup fixturing and sometimes with the use of advanced sensing (touch, vision, arc monitoring, etc.) tools, productivity can increase drastically.
- Higher Quality Welding Requirements: This type of welding equipment can produce consistent welding in an extremely repeatable fashion as well as much quicker than manual welding operations. Having a more consistent weld means your weld quality will increase while reducing the number of welding defects.
- Cost Of Welding Robots: With the cost of welding robots decreasing, using welding equipment like cobots, or companies purchasing robots as a monthly service, this is making them more affordable to a broader range of welding industries.
- Welding Safety: Welding robots reduce the potential for people to put themselves in confined spaces, inhaling toxic welding fumes, exposure to arc flash, and even radiation. The fixability of being able to use a robot instead of a human is becoming more common in many welding applications now, saving manual welders from countless job hazards.
The trends in welding automation:
Below, I list some trends found in the welding automation market.
Collaborative Welding Robots: Collaborative welding robots, or cobots, can work safely alongside their human co-workers. Compared to traditional industrial robots, smaller cobots are becoming more popular because of their easy-to-program robot software and ability to quickly perform changeovers.
Machine Learning: Welding robots are becoming more intelligent from the great advancements in machine learning with the support of artificial intelligence (AI) software. These robots are more capable of adapting to their weld environment while performing more complex welding operations.
More Welding Exposure: Because this welding technology is becoming more common among many industries, and the cost of owning robots is starting to come down, this is making them more intriguing to many new industries. As these welding robots become more versatile and easier to program, they will be used in more variety of industries in the future.
Connect with weld engineering contractors on JOINER Services.
Are you looking to invest in welding automation products? Or perhaps you need an expert to help you with welding set-up and implementation? Whatever the case may be, JOINER Services can help you find the right person for the job.
Join for free and start searching for projects or engineer profiles today.
FAQs About Welding Automation
Below, I list some FAQs about welding automation.








