Let me start this article by saying that I have vast knowledge of the industrial robotic welding industry. I graduated in 2008 from Ferris State University with a degree in Welding Engineering Technology. After graduation, I worked for several years as a contract welding engineer for engineering service companies and was programming ABB, Motoman, Panasonic, Fanuc, Nachi, Kawasaki, and KUKA robots to weld, which qualifies me to be able to write this in-depth article.
Below, I will describe details about the robotic welding process, enjoy!
What is robotic welding?
When industrial robots are used to perform the welding processes, we call this robotic welding. Robotic welding can perform repetitive welding tasks that are either too dangerous, too fast, or just too time-consuming for human welders. These industrial robots can perform these welding jobs with more accuracy, consistency, and quality, which makes them essential to compete in today’s global marketplace.
The reason for adding welding robots to the manufacturing process is pretty clear; however, with any significant change in the production line, companies must have a detailed plan before implementing any robotic systems into their daily operations.
In this article, I’ll discuss things that every company needs to understand about robotic welding:

1. Robotic Welding Isn’t New:
Using industrial robots to weld is not new. Companies started using robotic welding sometime in the 1960s. Robotic automation started to revolutionize the automobile industry in the 1980s when the automotive companies started using robotic spot welding to build cars.
For more than fifty years, robotic welding has transformed the manufacturing process and improved production lines. It has gone from a luxury automation technology only for some companies to almost a required and essential technology that companies now must rely on to compete.
Robotic welding was a very niche automation innovation. Its early applications were limited by the technology, but throughout the years, robotic welding has seen major technological advancements, especially in computing power and its software. These improvements have turned welding robots from simple, programmable machines into incredibly sophisticated and advanced robotic systems.
2. Types of Robotic Welding:
Robots can perform several types of welding operations. Below, I list the 5 common types of robotic welding used in today’s industrial manufacturing processes:
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding Robots: Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) or MIG welding robots are some of the most commonly used industrial robots. Robot manufacturers are now designing them for speed and adaptability, making this process suitable for welding a wide range of materials and thicknesses. MIG welding robots are particularly favored in industrial manufacturing for their efficiency, cycle time, and the high-quality welds they can produce.
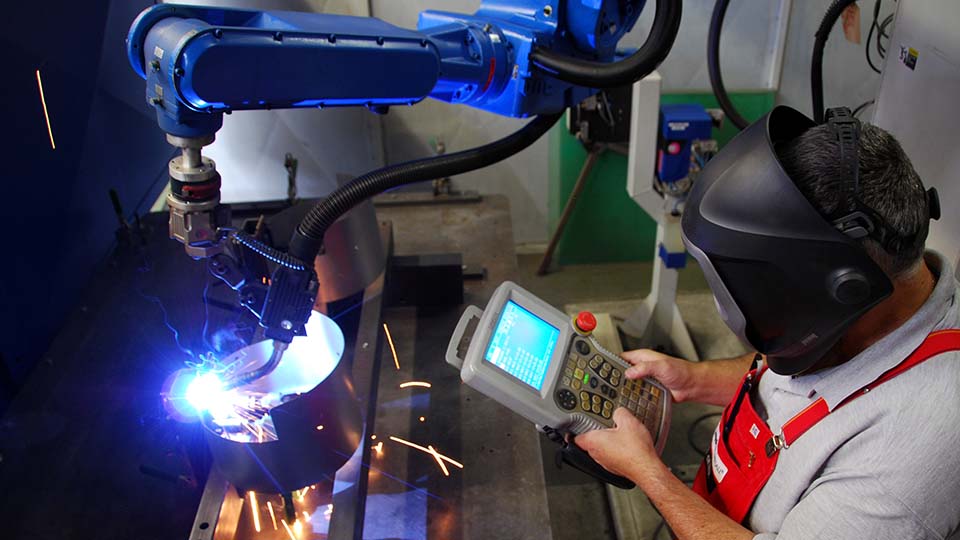

- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding Robots: Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) or TIG welding robots specialize in high-precision and high-quality products, and generally on “non-standard” materials. They are often used on products where aesthetics and weld integrity are crucial, but when cycle time is not so important. They can be used with or without the use of a filler material.
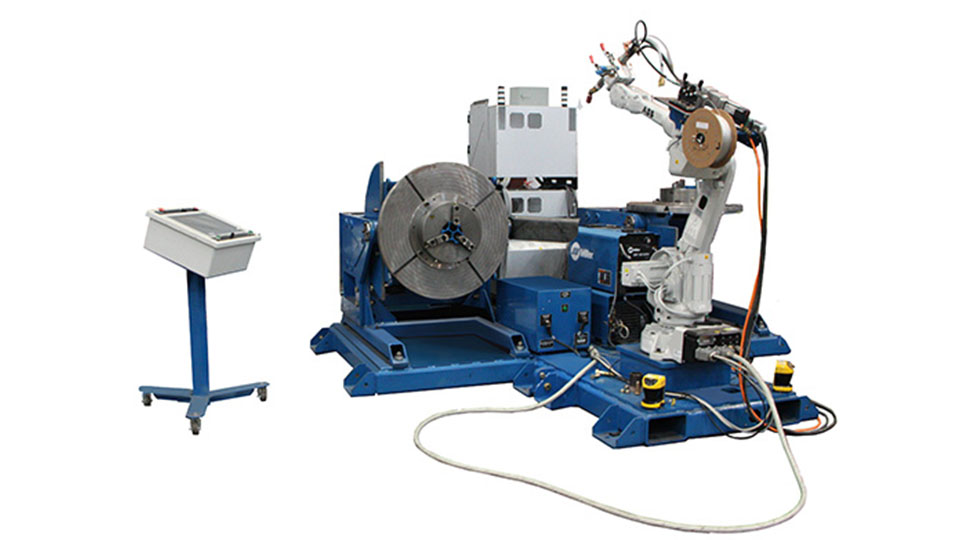
Picture credit to: Arc Specialties [1]
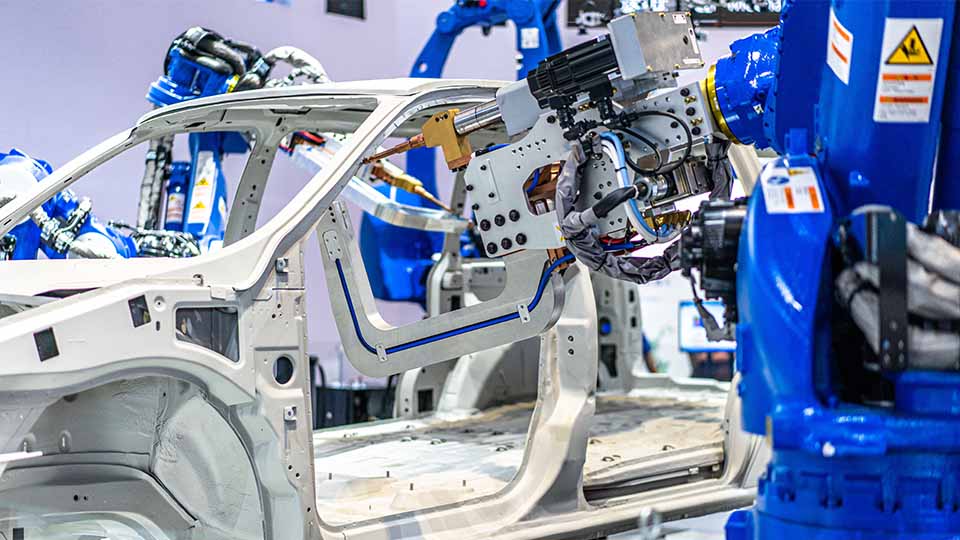
- Resistance Spot Welding (RSW) Robots: Resistance spot welding, often referred to as spot welding robots, are the go-to choice for fast and efficient joining of thin sheet metals. These welding robots are commonly used in automobile production lines, where they apply a precise pressure, add heat, for an amount of time to create strong, reliable welds in a fraction of the time it would take to manually do this process.
- Laser Beam Welding (LBW) Robots: Laser welding robots offer supreme precision and speed. The welding process works by directing a high-powered laser beam onto a tiny spot, achieving deep welds with very little material distortion. This makes them perfect for detailed tasks in electronics, medical equipment, and delicate automotive parts, where precision and speed is key.
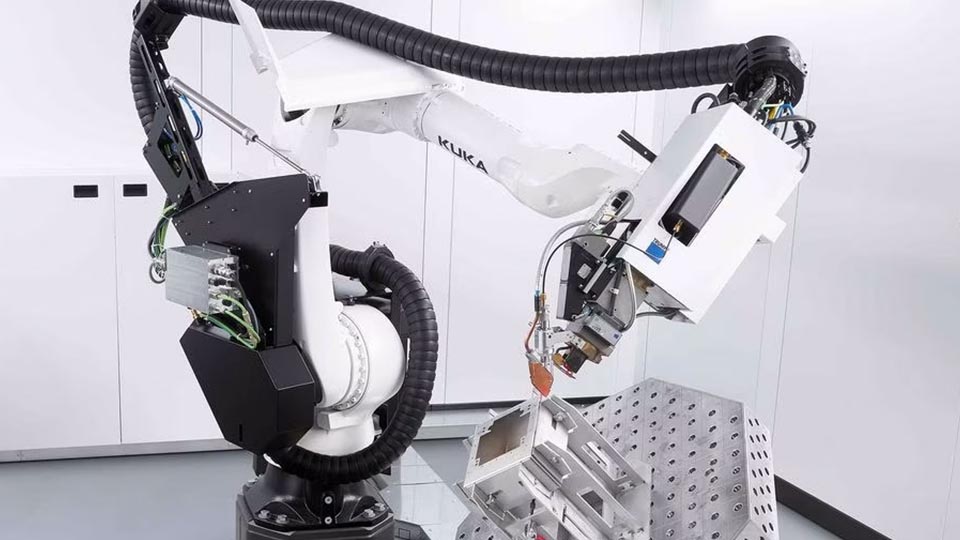

Picture credit to: Trumpf [2]
- Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) Robots: Plasma welding robots use a plasma arc to achieve high-quality welds with exceptional precision. This method is particularly effective for welding thin materials and for applications that require a controlled heat-affected zone.
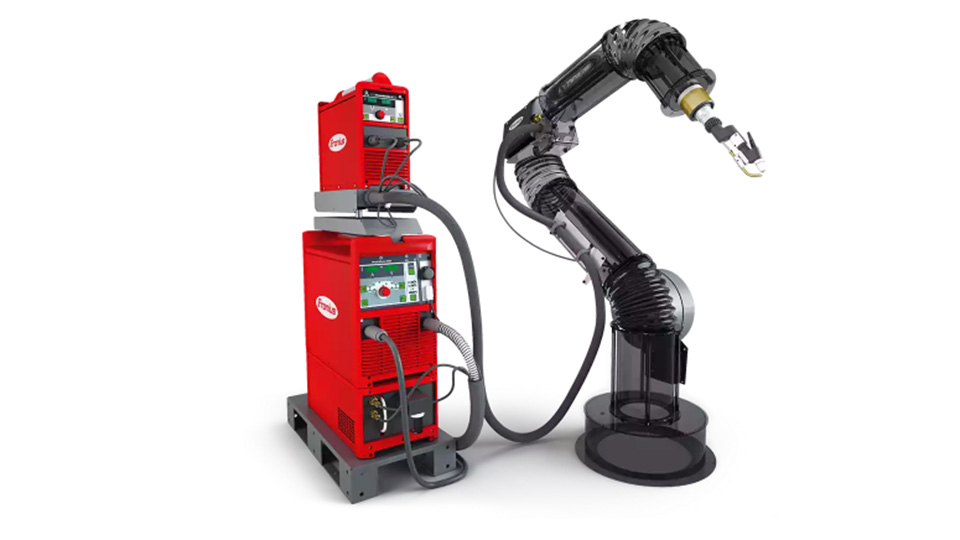

Picture credit to: Fronius [3]
3. Robotic Welding is Cheaper Than Manual Welding:
Starting with robot welding systems might seem like a big financial commitment upfront. You’re looking at costs for the robots themselves, plus the software they need, training for your team, and maybe some updates to the tooling and fixturing workspace.
However, these initial costs will not take long to pay off. Industrial welding robots will increase cost efficiency with increased on-time, reduced scrap material, a set list of weld parameters for each specific weld for increased quality control, and allowing for longer weld cycle times. All these savings will add up fairly quickly.
4. Robots Create Jobs:
When it comes to automation, there is always a fear of robots taking over human jobs. However, that is not necessarily true with robotics.
When robotic welding systems step in to handle the monotonous and risky jobs, they’re actually setting the stage for new, more advanced job opportunities for workers in areas like robot programming, maintenance, and overseeing the systems as an operator. These jobs require a more complex set of skills and usually come with better pay and working conditions.
Also, the increase in productivity that comes from using robotic welding can drive business growth, which ultimately leads to more job openings. This shift doesn’t diminish the value of human workers. Instead, it elevates their roles.
5. You Still Need Programming and Training:
There needs to be training for the existing workforce once a company introduces these robotic systems. The staff needs to understand how to operate, interact with, and maintain these industrial robot systems. It is difficult to find great hands-on robot programmer training courses, but it is important to find one that fits your worker’s technical skills and robotic equipment.
Once the robot is installed, it will need continuous support through touch-ups or reprogramming of weld points or moves if your company needs contract robot programming services to support production, look to JOINER Services to help support your project.
6. Robotic Welding Processes Produce Less Scrap:
With proper fixturing and the use of vision or tracking systems, less material gets wasted with robotic welding. This is because there are fewer errors during the welding process or start-and-stops that might be required compared with manual welding.
This ultimately improves a business’s profitability because of the increase in weld quality; therefore, fewer resources are being used for the same output, and it produces less scrap material.
7. Robotic Welding Equipment May Not Be Fit for Small Projects:
Robotic welding applications with smaller projects may be unreasonable. The initial setup cost for an industrial robotic welding system can be steep. For a large operation where the volume of work justifies the investment, these costs spread out over many projects, making the per-unit cost lower.
However, for smaller projects or operations, the math might not add up. The upfront expenses could outweigh the cost reductions a smaller operation may cost. Smaller projects may also come with more dramatic shifts in scope and project goals, which is something manual welders can more easily adapt to these dramatic shifts that small projects bring.
8. Robotic Welding Can Help Minimize Unplanned Downtime:
An advantage of robotic welding is less risk of unplanned downtime. Robots bring predictable and consistent performance that can help minimize downtime in manufacturing. Manual welders get fatigued or unfocused at times, which can cause human errors, that lead to mistakes that cause downtime.
These robotic systems are designed so you can easily implement a preventative maintenance schedule, which can be conducted during non-production hours. Many of these industrial robots also have advanced software that provides early warnings about machinery issues or replacement parts.

The Benefits of Robotic Welding:
Robotic welding does offer several advantages over traditional manual welding methods. These benefits include:
- Industrial robots can be used in dangerous areas where humans may not be able to go.
- The return on investment (ROI) can be anywhere from one to three years.
- Decreased welding cycle times.
- Increased welding productivity or up-time.
- Larger parts can be welded in a single pass or multipass without stopping or adjusting the part.
- Using cameras, sensors, and tracking tools, the welded parts will be highly consistent which helps improve the quality of the product.
According to a study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) [4], a human welder cannot keep their welding torch on the work more than 30% of the time. However, a robotic welding machine can keep its torch on the work about 90% of the time. Even though the robot welder cannot weld any faster than a human, it can produce about 3 times as much work as its human counterpart.
What are the hazards of robotic welding?
Robotic welding has many types of hazards that can occur during the process. It is extremely important to follow robot safety and welding safety guidelines to reduce the number of accidents and keep employees safe.
Below, I have listed some of the major hazards when robotic welding.
Welding Hazards:
- Arc flash causing eye wounds
- Exposure to metal fumes
- Ultraviolet radiation (UV)
- Skin burns
- Electrical shock
- Fire hazard
Robotic Hazards:
- Tool Center Point (TCP) not properly setup
- Lack of collision detection in the robot
- Improper fixturing or clamping of the workpiece
- Pinch points or crushed body parts
Performing an annual risk assessment of your robotic and welding equipment will help reduce accidents and near misses. Properly training staff on the dangers of industrial robots and the risks associated with the welding process is highly recommended on an annual basis.

Connecting With Engineering Contractors:
Hiring an in-house robotic welding engineer is not always easy for everyone.
This is where JOINER Services comes in. It is a platform where you can find the best self-employed contract weld engineers for your robotic welding processes. On JOINER, you have access to thousands of vetted engineers across multiple states with the skills and experience you need.

Join for free and start searching for the right engineer today!
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
Below, I list some FAQs about robotic welding.
Data Resources:
- [1] https://www.arcspecialties.com/product/robotic-hotwire-gtaw-system-with-two-positioners/
- [2] https://www.trumpf.com/en_US/products/machines-systems/laser-welding-systems-and-the-arc-welding-cell/trulaser-weld-5000/
- [3] https://www.fronius.com/en/welding-technology/products/robotic-welding/plasma-welding/plasma/plasma
- [4] https://tsapps.nist.gov/publication/get_pdf.cfm?pub_id=820148








